Openstack 30分钟概要介绍 regexisart
如需转载,请标明原文出处以及作者
陈锐 RuiChen @kiwik
2014/5/30 20:04:51
写在最前面:
本来是一份培训资料,也花了些时间收集资料,删了可惜,索性发篇blog。
What is OpenStack?
The kernal of Cloud OS, IaaS
It is a Cloud Computing Platform, establish a consistent model for different virtualization include compute, network, storage, providing users with unified API.
OpenStack is not?
OpenStack is not a virtualization hypervisor.
Core Modules
Include all parts of Cloud OS.
- Nova -> compute
- Cinder -> block storage
- Neutron -> network
- Keystone -> identity
- Glance -> image
- Horizon -> dashboard
- Heat -> orchestration
- Ceilometer -> telemetry
- Swift -> object storage
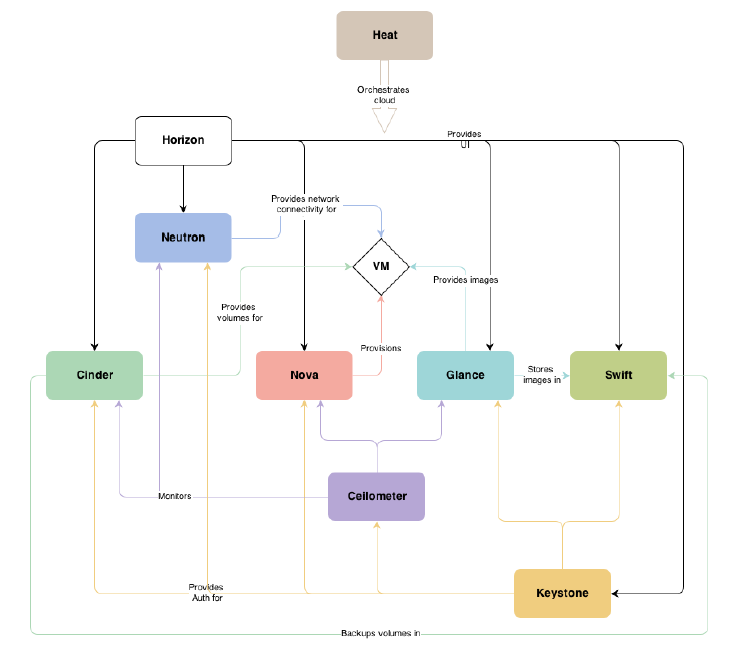
logical view
This is logical view of OpenStack.
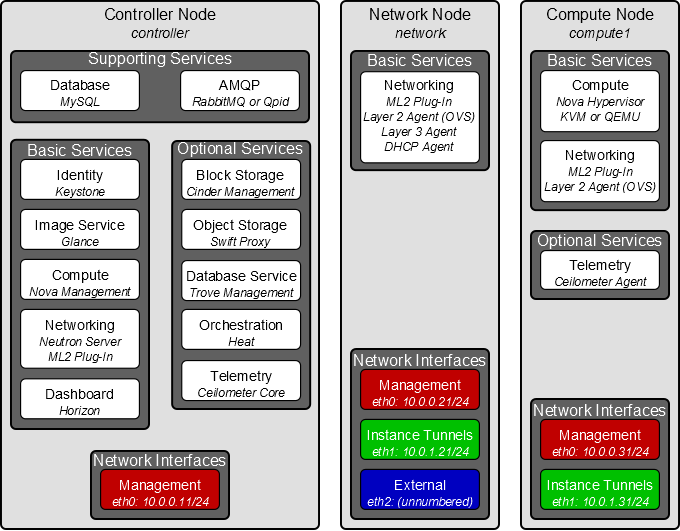
deployment view(3 nodes)
Nova
Nova is cloud computing controller. It is designed to manage and automate pools of computer resources and can work with widely available virtualization technologies.
Nova has an abstraction layer for compute drivers.
include:
- group A(fully supported and tested):
- KVM/QEMU via libvirt
- group B(partly supported and tested):
- Hyper-V
- XenServer
- VMWare
- group C(minimal testing and at risk):
- Docker
- Xen via libvirt
- LXC via libvirt
libvirt: A toolkit to interact with the virtualization capabilities.
Nova’s architecture is designed to scale horizontally on standard hardware with no special hardware or software requirements and provide the ability to integrate with legacy systems and third-party technologies.
Manages the lifecycle of compute instances in an OpenStack environment. Responsibilities include spawning, scheduling and destroying of virtual machines.
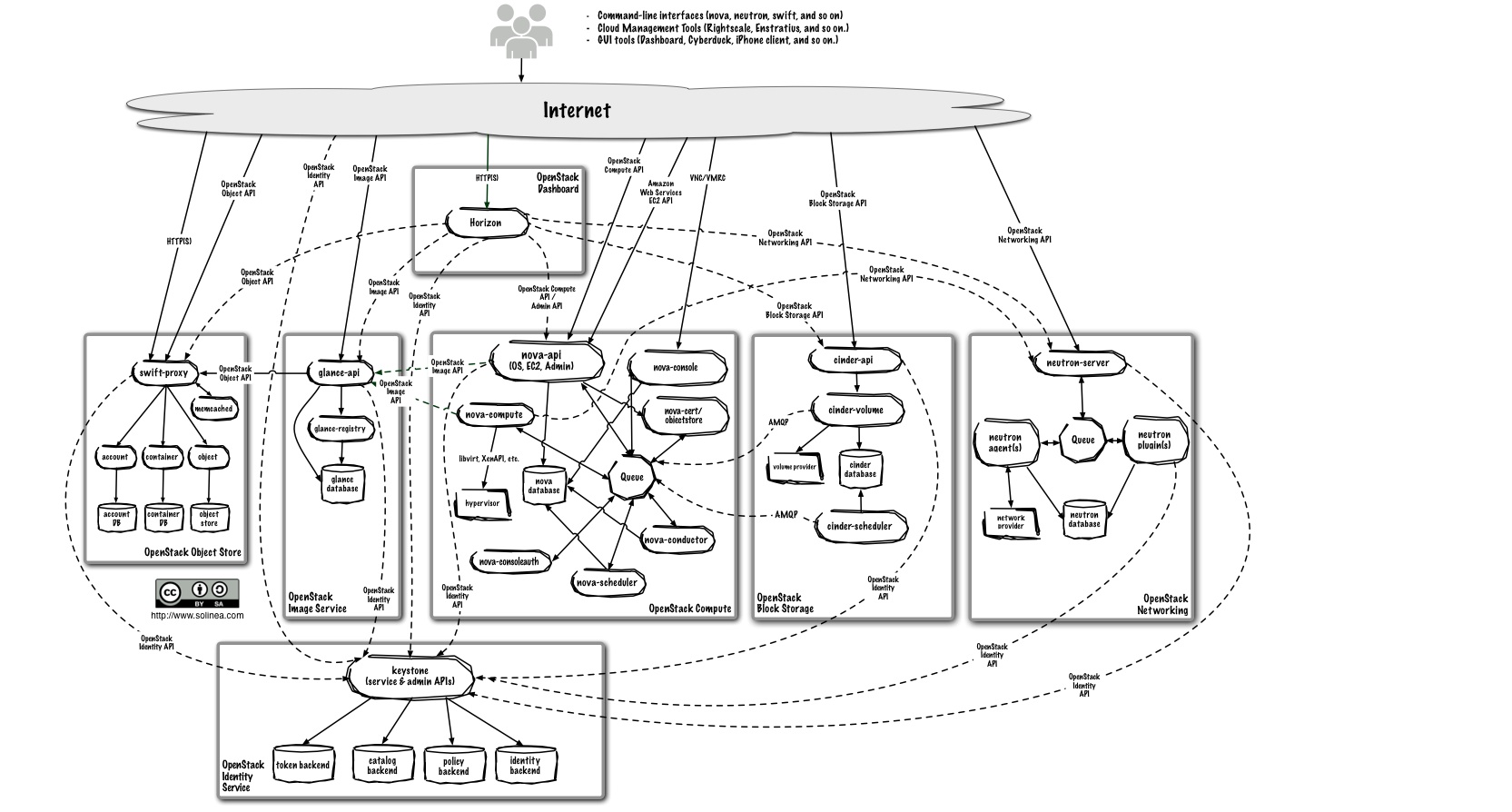
include core modules:
- nova-api
- nova-scheduler
- nova-compute
- nova-cert
- nova-conductor
- nova-consoleauth
- nova-novncproxy
nova-api
Handle http request, endpoint of Nova.
- nova-os-api
- nova-ec2-api
- nova-metadata-api
nova-os-api: handle OpenStack REST type api request.
POST v2/{tenant_id}/servers
{
"server":{
"name":"server-test-1",
"imageRef":"b5660a6e-4b46-4be3-9707-6b47221b454f",
"flavorRef":"2",
"max_count":1,
"min_count":1,
"networks":[
{
"uuid":"d32019d3-bc6e-4319-9c1d-6722fc136a22"
}
]
}
}
nova-ec2-api: handle nova compatible AWS EC2 api request.
http://127.0.0.1:8773/?Action=RunInstances
&ImageId=ami-2bb65342
&MaxCount=1
&MinCount=1
&Placement.AvailabilityZone=us-east-1b
&Monitoring.Enabled=true
&AWSAccessKeyId=0GS7553JW74RRM612K02EXAMPLE
&Version=2014-02-01
&Expires=2010-10-10T12:00:00Z
&Signature=lBP67vCvGlDMBQ1dofZxg8E8SUEXAMPLE
&SignatureVersion=2
&SignatureMethod=HmacSHA256
nova-metadata-api: handle instance metadata request, work with cloud-init, cfntools and user script.
GET http://169.254.169.254/openstack/2012-08-10/meta_data.json
{
"uuid":"d8e02d56-2648-49a3-bf97-6be8f1204f38",
"availability_zone":"nova",
"hostname":"test.novalocal",
"launch_index":0,
"meta":{
"priority":"low",
"role":"webserver"
},
"public_keys":{
"mykey":"ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAAAgQDYVEprvtYJXVOBN0XNKVVRNCRX6BlnNbI+USLGais1sUWPwtSg7z9K9vhbYAPUZcq8c/s5S9dg5vTHbsiyPCIDOKyeHba4MUJq8Oh5b2i71/3BISpyxTBH/uZDHdslW2a+SrPDCeuMMoss9NFhBdKtDkdG9zyi0ibmCP6yMdEX8Q== Generated by Nova\n"
},
"name":"test"
}
nova-scheduler
Takes a virtual machine instance request from the queue(AMQP) and determines on which compute server host it should run. Intersection of the hosts matched with all filters will be selected.
Scheduler policy can be configured.
- AvailabilityZoneFilter
- RamFilter
- DiskFilter
- CoreFilter
- DifferentHostFilter
- AggregateMultiTenancyIsolationFilter
- …
nova-compute
A worker daemon that creates and terminates virtual machine instances through hypervisor APIs. It dispatch the message to hypervisor.
For example, request chain of booting a instance:
request -> nova-compute -> libvirt -> QEMU/KVM
nova-cert
Manages x509 certificates, include: cert.pem and pk.pem. Work with EC2 request, for example, ec2tools command ec2-bundle-vol, creates an instance image by compressing, encrypting, and signing a copy of the root device volume for the instance.
ec2-bundle-vol -d /mnt -k pk-HKZYKTAIG2ECMXYIBH3HXV4ZBEXAMPLE.pem -c cert-HKZYKTAIG2ECMXYIBH3HXV4ZBEXAMPLE.pem -u 111122223333 -r x86_64
nova-conductor
Mediates interactions between nova-compute and the database. Aims to eliminate direct accesses to the cloud database made by nova-compute, and run some long time tasks, for example: live-mirgate, resize and boot.
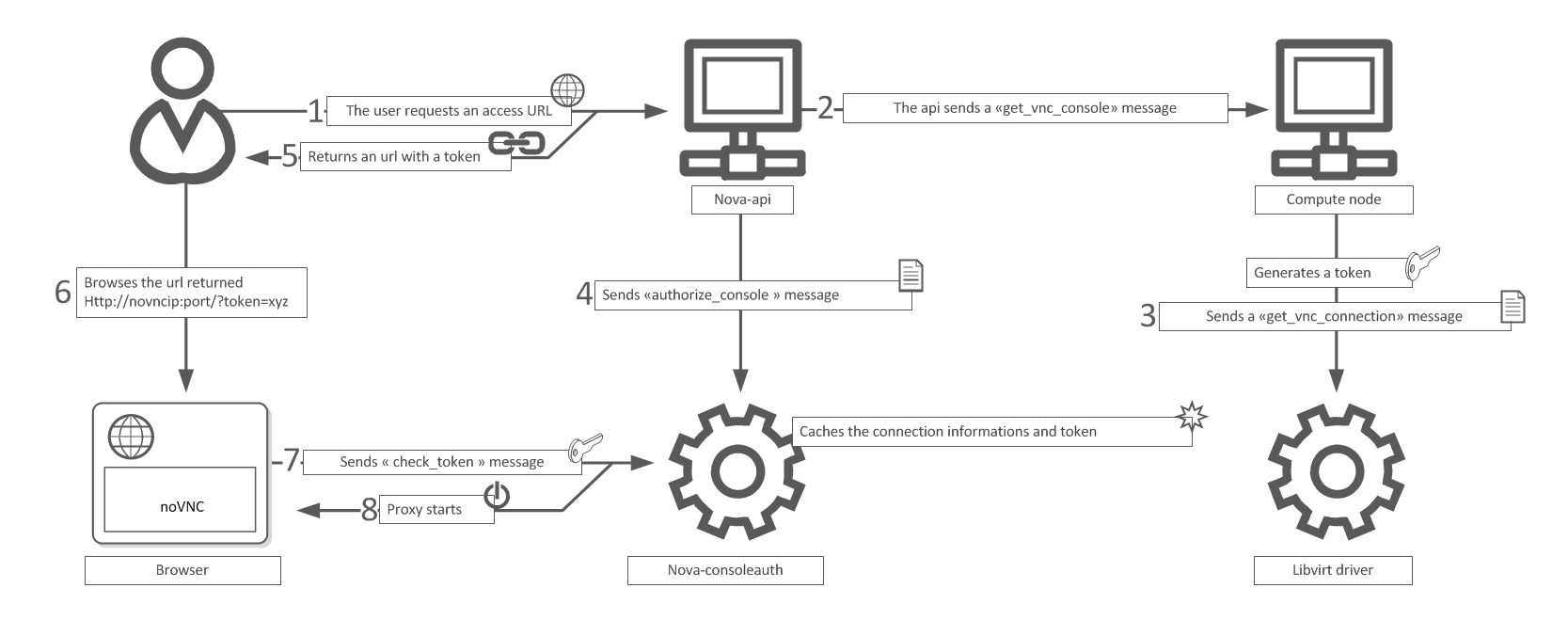
nova-novncproxy
Provides a proxy for accessing running instances through a VNC connection. Supports browser-based novnc clients.
nova-consoleauth
Authorizes tokens for users that console proxies provide.
nova get-vnc-console vm1 novnc
http://192.168.28.4:6080/vnc_auto.html?token=f5abd84d-708f-4486-af61-40c6e5a876c0
vnc workflow
Cinder
Cinder provides persistent block-level storage devices for use with OpenStack compute instances. The block storage system manages the creation, attaching and detaching of the block devices to servers. Block storage volumes are fully integrated into OpenStack Compute. This service is similar to the AWS EC2 Elastic Block Storage (EBS) offering.
Pluggable driver architecture is used in Cinder. In addition to LVM (logical volume manager), it can use storage platforms including Huawei FusionStorage, Ceph, EMC, GlusterFS, IBM Storage, NetApp, HP Storage and so on.

include core modules:
- cinder-api
- cinder-scheduler
- cinder-volume
- cinder-backup
cinder-api
Like nova-os-api, handle OpenStack REST type API request.
POST v2/{tenant_id}/volumes
{
"volume":{
"availability_zone":null,
"source_volid":null,
"display_description":null,
"snapshot_id":null,
"size":10,
"display_name":"my_volume",
"imageRef":null,
"volume_type":null,
"metadata":{
}
}
}
cinder-scheduler
Like the nova-scheduler, picks the optimal block storage provider node(cinder-volume) on which to create the volume. Intersection of the hosts matched with all filters will be selected.
Scheduler policy can be configured.
- AvailabilityZoneFilter
- CapacityFilter
- CapabilitiesFilter
- …
cinder-volume
Responds to requests, interacting with other processes (like cinder-scheduler) through a message queue(AMQP). It can interact with a variety of storage providers through a driver architecture.
- Huawei FusionStorage Driver
- Ceph Driver
- LVM Driver
- EMC Driver
- …
cinder-backup
A backup is a full copy of a volume stored in an external service. A backup can be restored from the external service to either the same volume that the backup was originally taken from, or to a new volume.
External service:
- Ceph
- Swift
Neutron
Neutron is a system for managing networks and IP addresses. Enables network connectivity as a service for other OpenStack services, such as OpenStack Compute. Provides an API for users to define networks and the attachments into them.

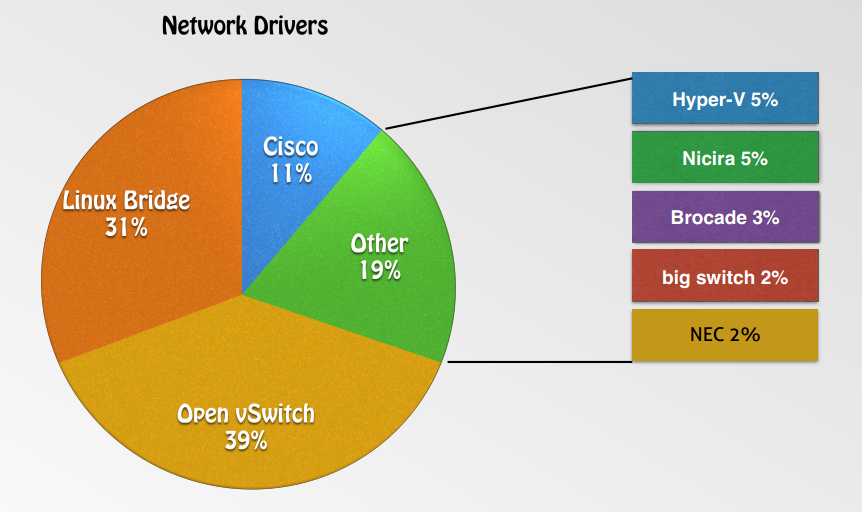
Has a pluggable architecture that supports many popular networking vendors and technologies.
- Open vSwitch
- Linux Bridge
- Cisco Nexus
- Modular Layer 2(ML2)
- Big Switch Controller Plugin
- …
include core modules:
- neutron-server
- neutron-dhcp-agent
- neutron-plugin-*-agent
- neutron-L3-agent
neutron-server
Accepts and routes API requests to the appropriate OpenStack Networking plug-in for action.
POST v2.0/subnets
{
"subnet":{
"subnet":{
"network_id":"d32019d3-bc6e-4319-9c1d-6722fc136a22",
"ip_version":4,
"cidr":"192.168.199.0/24"
}
}
}
neutron-dhcp-agent
Dynamic host IP addressing, using Dnsmasq. Assign IP addresses to virtual machines.
neutron-plugin-*-agent
Plugs and unplugs ports, creates networks or subnets. These plug-ins differ depending on the vendor and technologies used in the particular cloud. For example, Open vSwitch, ML2, LinuxBridge.
neutron-L3-agent
It uses the Linux IP stack and iptables to perform L3 forwarding and NAT. In order to support multiple routers with potentially overlapping IP addresses, neutron-L3-agent defaults to using Linux network namespaces to provide isolated forwarding contexts.(SNAT/DNAT)
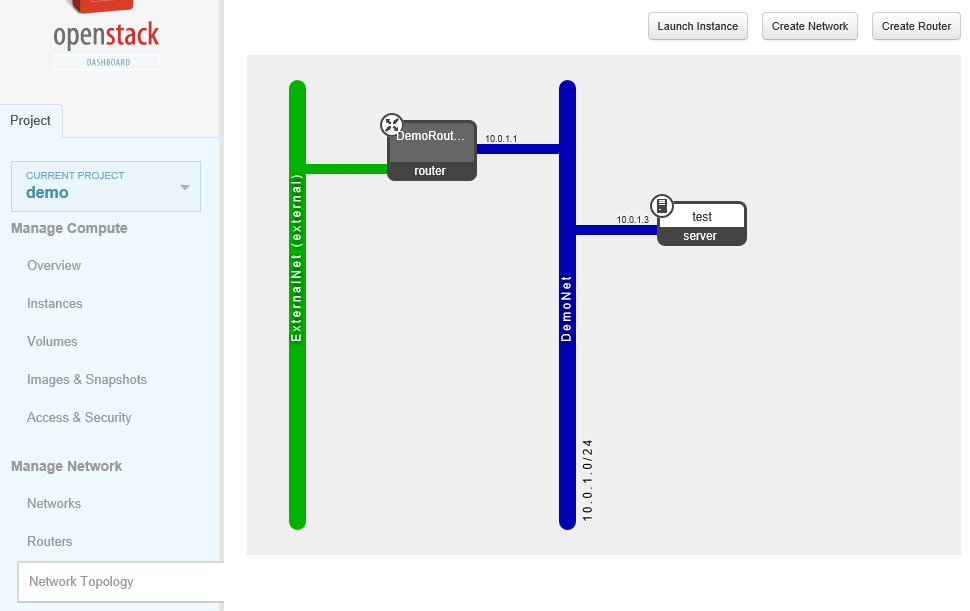
How to using Neutron?
classic steps
- create external network
- create subnetA(20.0.2.0/24) in external network as floating ip pool
- create internal network
- create subnetB(10.0.1.0/24) in internal network
- create router
- set router gate-way, associate with external network
- add router interface, associate with internal network
- boot instance in internal network
- associate floating ip to instance(SNAT/DNAT)
- access to instance from external network
logic topology
Keystone
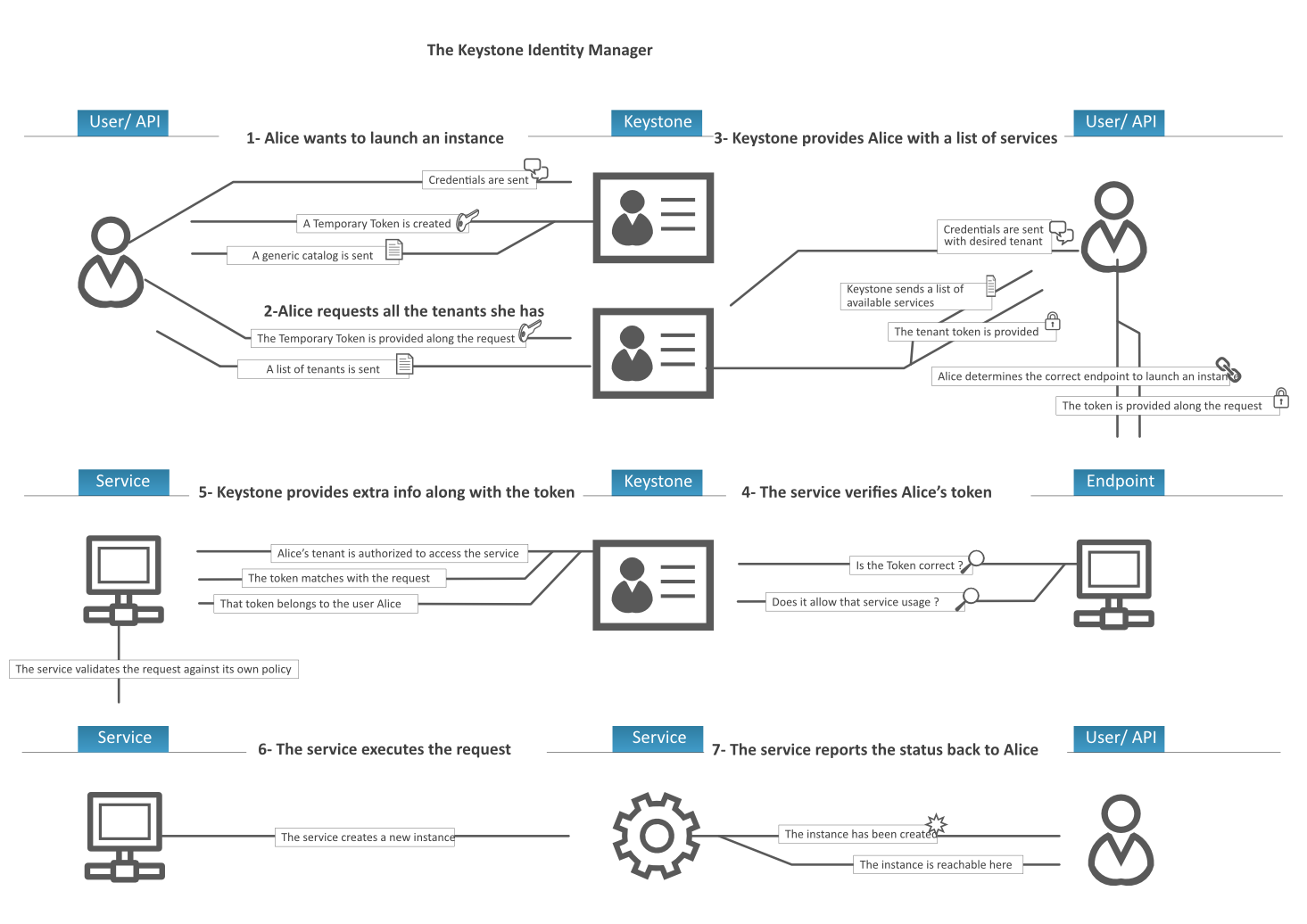
Keystone provides a central directory of users mapped to the OpenStack services they can access. It acts as a common authentication system across the cloud operating system.
It supports multiple forms of authentication including standard username and password credentials, token-based systems and AWS-style (i.e. Amazon Web Services) logins.
Additionally, the catalog provides a queryable list of all of the services deployed in an OpenStack cloud in a single registry. Users and third-party tools can programmatically determine which resources they can access.

core concepts
- user
- project(tenant)
- role
- token
Projects are organizational units in the cloud to which you can assign users. Projects are also known as tenants. Users can be members of one or more projects. Roles define which actions users can perform. You assign roles to user-project pairs.
issue token
POST /v3/auth/tokens
{
"auth":{
"identity":{
"methods":[
"password"
],
"password":{
"user":{
"id":"0ca8f6",
"password":"secrete"
}
}
},
"scope":{
"project":{
"id":"263fd9"
}
}
}
}
classic workflow:
Heat
Heat provides a template-based orchestration for describing a cloud application by running OpenStack API calls to generate running cloud applications.
The software integrates other core components of OpenStack into a one-file template system. The templates enable you to create most OpenStack resource types, such as instances, floating IPs, volumes, security groups, users, and so on.
logic view
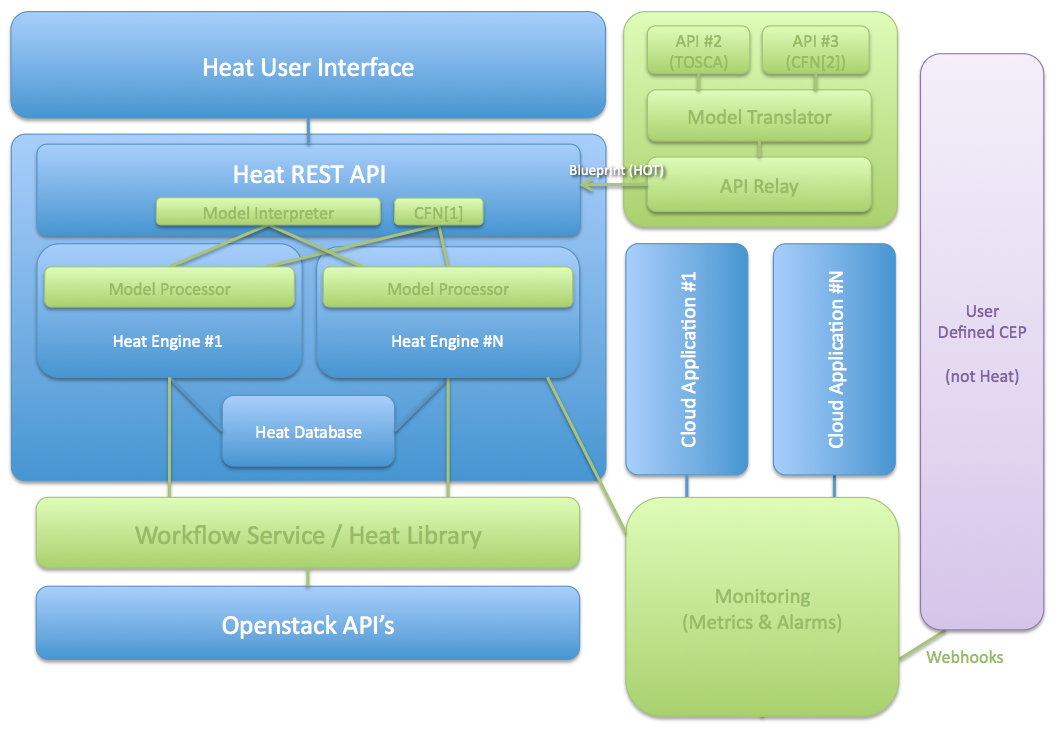
TOSCA: Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications
CFN: AWS CloudFormation
CEP: Complex event processing
include core modules:
- heat-api
- heat-api-cfn
- heat-api-cloudwatch
- heat-engine
heat-api
Provides an OpenStack native REST API that processes API requests by sending them to the heat-engine over RPC.
POST v1/{tenant_id}/stacks
{
"stack_name": "{stack_name}",
"template_url": "{template_url}",
"parameters": {
"param_name-1": "param_value-1",
"param_name-2": "param_value-2"
},
"timeout_mins": "{timeout_mins}"
}
heat-api-cfn
Provides an AWS Query API that is compatible with AWS CloudFormation and Processes API requests by sending them to the heat-engine over RPC.
https://127.0.0.1:8000/
?Action=CreateStack
&StackName=MyStack
&TemplateBody=[Template Document]
&Parameters.member.1.ParameterKey=AvailabilityZone
&Parameters.member.1.ParameterValue=us-east-1a
&Version=2010-05-15
&SignatureVersion=2
&Timestamp=2010-07-27T22%3A26%3A28.000Z
&AWSAccessKeyId=[AWS Access KeyID]
&Signature=[Signature]
heat-api-cloudwatch
This implements an approximation of the AWS CloudWatch API and translates it into a native representation. It then calls the heat-engine via AMQP RPC to implement them.
http://127.0.0.1:8003/?SignatureVersion=2
&Action=ListMetrics
&Version=2010-08-01
&AWSAccessKeyId=<Your AWS Access Key Id>
&SignatureVersion=2
&SignatureMethod=HmacSHA256
&Timestamp=2010-11-17T05%3A13%3A00.000Z
This feature will be deprecated or removed during the Havana cycle as we move to using Ceilometer as a metric/alarm service instead.
heat-engine
Orchestrates the launching of templates and provides events back to the API consumer.
Heat template
# This is a hello world HOT template just defining a single compute instance
heat_template_version: 2013-05-23
description: >
Hello world HOT template that just defines a single compute instance.
Contains just base features to verify base HOT support.
parameters:
KeyName:
type: string
description: Name of an existing key pair to use for the instance
InstanceType:
type: string
description: Instance type for the instance to be created
default: m1.small
constraints:
- allowed_values: [m1.tiny, m1.small, m1.large]
description: Value must be one of 'm1.tiny', 'm1.small' or 'm1.large'
ImageId:
type: string
description: ID of the image to use for the instance
resources:
my_instance:
# Use an AWS resource type since this exists; so why use other name here?
type: AWS::EC2::Instance
properties:
KeyName: { get_param: KeyName }
ImageId: { get_param: ImageId }
InstanceType: { get_param: InstanceType }
outputs:
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [my_instance, PublicIp] }
Ceilometer
The project aims to become the infrastructure to collect measurements within OpenStack. Its primary targets are monitoring and metering. Monitors and meters the OpenStack cloud for billing, benchmarking, scalability, and statistical purposes.
logic view
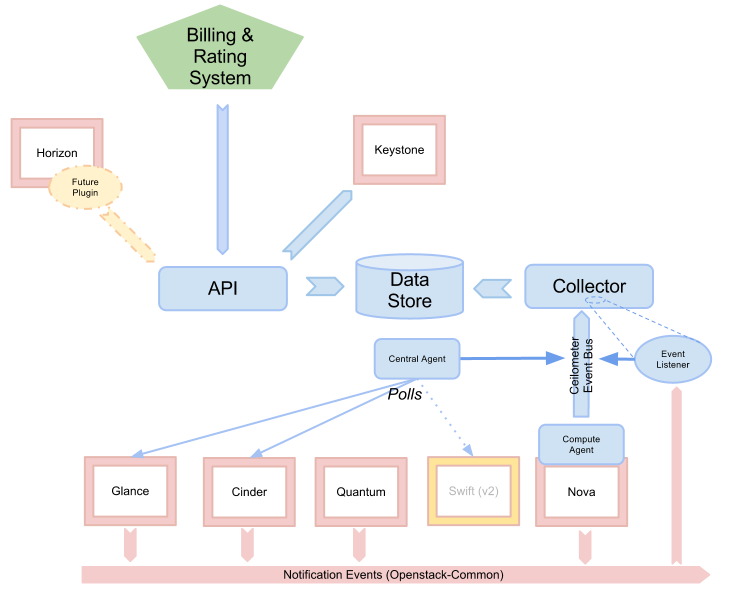
include core modules:
- ceilometer-api
- ceilometer-agent-central
- ceilometer-agent-compute
- ceilometer-collector
ceilometer-api
Runs on one or more central management servers to provide access to the data from the data store.
GET v2/meters/{meter_name}
{
"counter_name": "instance",
"counter_type": "gauge",
"counter_unit": "instance",
"counter_volume": 1.0,
"message_id": "5460acce-4fd6-480d-ab18-9735ec7b1996",
"project_id": "35b17138-b364-4e6a-a131-8f3099c5be68",
"resource_id": "bd9431c1-8d69-4ad3-803a-8d4a6b89fd36",
"resource_metadata": {
"name1": "value1",
"name2": "value2"
},
"source": "openstack",
"timestamp": "2013-11-21T12:33:08.323533",
"user_id": "efd87807-12d2-4b38-9c70-5f5c2ac427ff"
}
ceilometer-agent-central
Runs on a central management server to poll for resource utilization statistics for resources not tied to instances or compute nodes. For example: network, subnet, floating ips, volume and so on.
ceilometer-agent-compute
Runs on each compute node and polls for resource utilization statistics. There may be other types of agents in the future, but for now we will focus on creating the compute agent. Using libvrit, Hyper-V and VMware API. For example: CPU Stats, Network Stats, Disk Stats and so on.
ceilometer-collector
Runs on one or more central management servers to monitor the message queues (for notifications and for metering data coming from the agent). Notification messages are processed and turned into metering messages and sent back out onto the message bus using the appropriate topic. Telemetry messages are written to the data store without modification.